Did you know that Arabic is the fifth most common primary language in the world?
There are approximately 313 million people who speak Arabic. That number increases to 422 million people when you include non-native speakers or those who speak Arabic as a secondary language. The only languages that are more widely spoken are Mandarin, English, Hindi, and Spanish.
In this post, we’re going to discuss the Arabic language in use today. You’ll learn which countries speak Arabic as a primary language and about countries where Arabic is a recognized minority language. We’ll also discuss countries where there are large populations of Arabic speakers, though it is not a primary language.
We’ll break this down a bit so that you understand the demographics of these countries, the population of Arabic speakers, and the dialect of Arabic you’ll find in different locations.
Arabic Dialects in Use Today
Arabic is in the same language family as Aramaic, an ancient language that is still in use in some areas today. Throughout time, the ancient language has influenced many cultures and you can find roots of Arabic in several regions.
The Island of Sicily, for instance, has its own language (Sicilian) which residents are currently trying to preserve. As part of Italy, the recognized language taught is school is now traditional Italian. The Sicilian language has many root words that are Arabic and Greek in origin, from different eras in history where these people occupied the land.
Arabic is also a primary or recognized language in many parts of the world. In these different regions, the language has developed with influences from the people in those areas. This results in many different dialects which are related, and often understandable to other Arabic speakers, but still distinct in their own right.
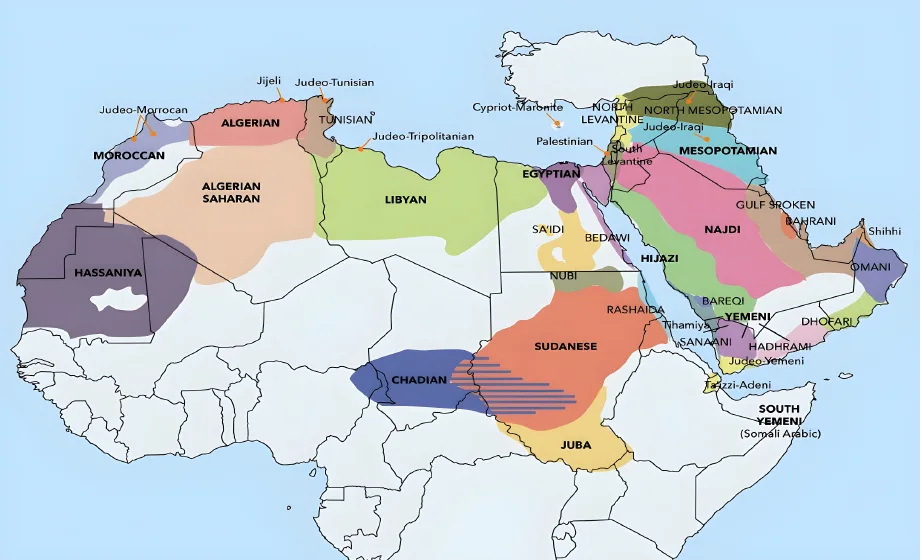
There are many dialects of Arabic spoken today, but they are divided into a few main categories. These include Classical Arabic also called Quranic, Modern Standard Arabic, and Colloquial Arabic.
Classical Arabic
Classical Arabic has spoken in the 7th-9th centuries AD. This is also called Quranic because it’s the form of Arabic that the Quran was written in and it’s the standard literary form for the language. This is the language used in religious texts, as well as some fiction and poetry.
Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic is the currently recognized and taught form of the language. This is the language used in education and written communication by Arab speakers. It would be the form of Arabic that you’re most familiar with in business dealings or any formal communication.
Modern Standard Arabic is used in trade, business correspondence, and the language most professional texts adhere to, such as books or content used by Universities. This is also a standard dialect and many Arabic speakers do use Modern Standard Arabic, but pronunciations often differ. As with any language, regions, backgrounds, and influences will alter the way words are spoken.
Colloquial Arabic
This is the daily Arabic or the specific dialect used in the region. There are many dialects, and some are very similar to each other. However, some differ so drastically that they can be difficult to understand, even to native speakers of a different dialect.
The most common of colloquial Arabic dialects are Egyptian, Maghrebi, and Gulf.
The Egyptian dialect is spoken in Egypt. Because this dialect is often used in media, such as television shows and movies, it’s very commonly used in the Arabic-speaking world. It’s also well understood, even by those who speak a different dialect. There are other language traditions mixed into the Egyptian dialect, such as Turkish and English.
Maghrebi is another very popular dialect. Also called Darija or Derja, the language continuously changes, and new terms are added to the lexicon. The dialect has adopted Modern Standard Arabic terms, as well as other languages that include Italian and French.
The Gulf dialect is popular in the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Kuwait, Qatar, and some parts of Saudi Arabia. You’ll find that different areas use their own terminology. In essence, the Gulf dialect is a collection of dialects that are similar to each other, but with some distinctly geographic terms depending on where you are.
Countries Where Arabic Is the Primary Language
As a primary language, Arabic is popular in the Middle East, Africa, and Asia. The history of the Arabic language is rich and long. Historians believe that what we know as Arabic today is derived from Aramaic. There are about thirty different varieties of Arabic and various dialects.
Modern Standard Arabic is taught and understood in school and what’s primarily used in business dealings.
Arabic is the official language of twenty-two countries and all of these countries also are members of the Arab League, with the exception of Chad (which holds Observer Status).
- The dialect spoken in Algeria is called Algerian Arabic or Darja. It’s similar to Tunisian and Moroccan Arabic. Other dialects in Algeria include Eastern Algerian Arabic and Western Algerian Arabic.
- Bahrani Arabic, also called Baharna Arabic, is common in Bahrain. It’s also spoken in Eastern Arabia and Oman.
- The Chadian Arabic dialect is also called Shuwa or Shua Arabic. It’s also called Western Sudanic Arabic.
- There are several dialects spoken in Comoros. The Shingazija dialect is the one that’s most common. Other dialects used in this country include Shimwali, Moheli, and Shinzwani.
- Djibouti has two different official languages – French and Arabic. The Arabic dialect is Ta’izzi-Adeni, also referred to as Djibouti Arabic.
- In Egypt, the language is called Egyptian or Egyptian Arabic. The most common dialect is Masri.
- Mesopotamian Arabic is the most common Arabic language spoken in Iraq.
- The Jordanian dialect is Levantine Arabic. There are different languages that influence this dialect of Arabic, including English and Turkish.
- In Kuwait, the dialect spoken most frequently is called the Gulf Arabic dialect.
- Lebanon’s most popular dialect is Levantine Arabic, which is also common in Syria and western Jordan.
- Like many Arabic-speaking countries, the official language here is Modern Standard Arabic. The dialects most frequently used in Libya are Libyan Arabic, Tunisian Arabic, and Egyptian Arabic.
- In Mauritania, the dialect of Arabic is Hassaniya.
- Morocco’s most popular dialect is Darija. This is most similar to the dialects of Tunisia and Algeria.
- The Omani Arabic dialect is the most commonly spoken here, and it’s also spoken in a few of the regions near Oman.
- The dialect of Qatar is known as Qatari, sometimes called Gulf Arabic.
- Saudi Arabia. Peninsular Arabic is the dialect spoken in Saudi Arabia and a great deal of the Arabian Peninsula. Other countries that use this dialect include Southern Iran, Southern Iraq, Yemen, and Oman.
- While the official written language of Somalia is Arabic, most Somalis speak a language called Somali. It’s similar to Arabic but not identical. Most Somalis can read and write in Modern Standard Arabic because they study the Quran, which is written in this language.
- The Sudanese Arabic dialect is spoken in Sudan. The etymology of many of the words and phrases here is derived from the historical language of the region and includes both African and Arab influences.
- The most common dialects of Syria are Levantine Arabic and Damascus Arabic.
- The Tunisian dialect is called Derja. This is the most common dialect in this country.
- United Arab Emirates. Gulf Arabic is the most popular dialect in this country.
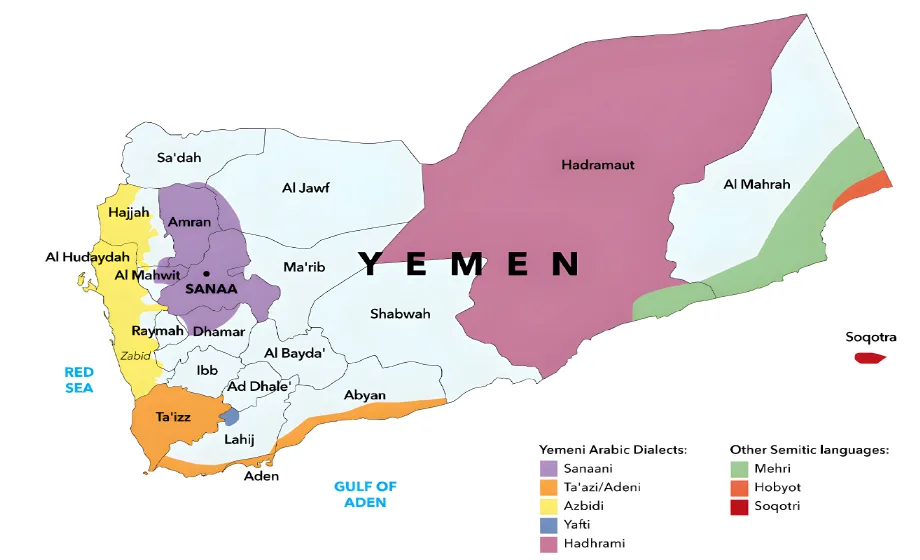
- The Yemeni dialect is spoken in Yemen and parts of Saudi Arabia
Added to these twenty-two countries, there are several regions where Arabic is one of the official languages.
These include:
- The Palestinian Territories. They are also part of the Arab League and Arabic is the primary language.
- Western Sahara. Hassaniya Arabic is the most common dialect here.
- This area has several dialects in common use which include Omani Arabic, Hadrami Arabic, and Standard Arabic.
Countries Where Arabic Is a Recognized Minority Language
Countries, where Arabic is the official language, are not the only places where Arabic is a popular primary language for residents. There are six places where Arabic is recognized as a minority language. Those include:
- Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic are both taught to Arabic-speaking children in school here. The most common dialect of Arabic in Iran is Khuzestani.
- Arabic speakers in Turkey may use several dialects. They include North Levantine Arabic and Mesopotamian Arabic.
- There are Arabic speakers in Niger and many other languages here. French is the official language of the area.
- In Senegal, one of the most common Arabic dialects is Hassaniya Arabic.
- Maghrebi Arabic and Classical Arabic are spoken in Mali.
- Cypriot Arabic is spoken in Cyprus, also called Sanna.
Countries Around the World with Residents Who Speak Arabic
The countries where Arabic is a recognized official language or secondary language are only the tip of the iceberg. There are over 400 million people who speak Arabic as a primary or secondary language. They live in countries around the world.
Countries with diverse populations, such as the United States, have a high population of those who speak Arabic as their native tongue. They also have citizens who learn Arabic as a secondary language. According to the New York Post, Arabic is currently the seventh most common non-English language spoken in homes in the United States.
The US has over 900,000 Arabic speakers, with the largest populations in big cities, such as New York and Chicago.
In the UK, Arabic is also gaining in popularity. With over 200,000 Arabic speakers, it’s the fifth most popular language in this area. There are over 6 million Arab speakers in Europe, with larger concentrations in Italy, Spain, Germany, and the Netherlands.
The Importance of Arabic in a World Economy
With the tremendous growth of the Arabic language around the world, it’s increasingly important to make room for this beautiful and historied language in business and in personal life. This is a fantastic secondary language for people who would like to access communication in other nations. It’s also personally used, as more and more citizens of the world are mobile. Native Arabic speakers now reside in most countries around the world.
Translating Arabic for people speaking other languages has become increasingly important in many industries. Whether you’re interested in making a menu accessible for more customers or translating an important business proposal, this language is key to opening new worlds of opportunity.